What is RFID technology?
How does radio identification work in practice?
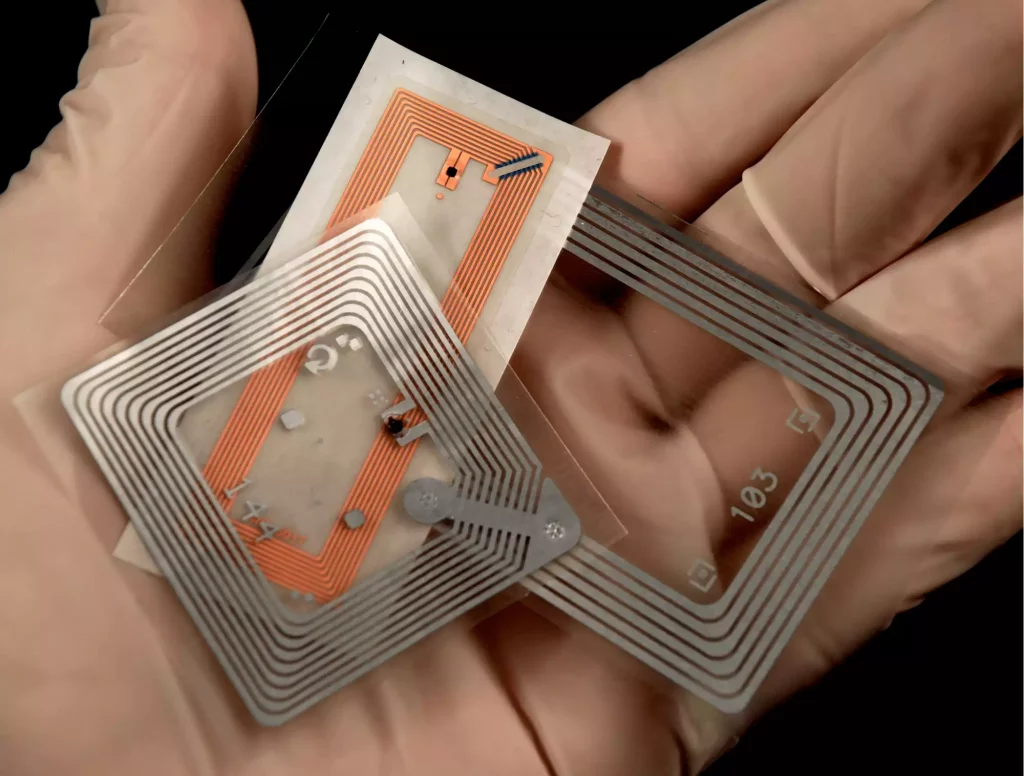
Behind the acronym RFID lies a simple concept: Radio Frequency Identification. The idea is to combine an RFID tag and a reader, enabling information to be transmitted remotely. In simple terms, the tag takes the form of a chip containing data, and a transmitter antenna that can be fixed or mobile. It uses radio waves to transmit its contents to the reader, enabling objects to be identified, assetsor people.
RFID technology in everyday life
Although we may not be aware of it, we are exposed to RFID technology on a daily basis. This is the case when we use contactless payment, when we visit Decathlon, or when we use our company badges.
But that's not all: RFID RFID is also widely used by professionals, in the luxury goods industry as well as in factories and warehouses, notably for asset tracking.
Advantages and disadvantages of RFID
The advantages of using it
RFID systems have brought a breath of fresh air to the world of identification, revolutionizing the way we manage our data. While barcodes and the more recent QR codes have long been the benchmark technologies in this field, RFID is proving to be far more effective and efficient.
So we like radio frequency identification for :
This technology does not require visual scanning. Unlike more traditional technologies, the RFID tag does not need to be seen by a reader. It simply has to be within a reasonable reading distance to be directly identified. A significant time-saver for your inventories!
A load of a hundred boxes passing through an RFID portal can be instantly detected by the system, saving you precious scanning time.
While this is not the case for all RFID systems, some of them can pinpoint tags on objects or people to within a meter. It's up to you to find the best balance between price and accuracy!
Yes: RFID can be used in a wide variety of sectors and applications! It is therefore extremely popular in hospitals, retirement homes, warehouses, factories, public transport, payment systems and anti-theft devices.
RFID tags are robust and able to withstand a wide range of environmental conditions, making them suitable for outdoor use too.
As companies strive for greater flexibility, RFID technology is a real ally. Not only does it save valuable time, it also makes companies more responsive, enabling them to make quick decisions, for example in the event of low stock levels. Improved customer satisfaction is the logical consequence of all these advantages.
A few limitations to note
As we've seen, RFID makes it possible to manage large quantities of data, over varying distances, securely and without complexity. However, such technology can also have its limitations if not properly implemented. For example:
This poses a risk to radio identification, as signals can be disrupted by metals or liquids. Fortunately, such interference is not systematic and depends on your environment. To avoid these pitfalls, it's essential to contact experts who can advise and guide you in your choice of solution.
If your RFID system isn' t properly dimensioned, distance constraints can hamper its operation. So when choosing your solution, it's important to define not only the accuracy you need, but also the maximum distance between tags and RFID readers.
One thing is certain: deploying RFID technology in your company is far from simple on a large scale. In fact, it requires the intervention of professionals like Solid Solutions in Identification, both to analyze and plan the locations of the elements, and to lay them out and make them functional.
To keep your system running at peak performance, maintenance may be essential. This is particularly the case for active RFID chips, where the battery will need changing after a few years.
Depending on the RFID technology you're considering, your budget can vary greatly. While passive chips are very affordable, their reading distance is reduced, and their storage capacity is limited. Conversely, you can opt for high-performance, more expensive active chips, whose lifespan is shortened by that of the built-in battery.
In short, it's all a question of balance!
RFID applications for professionals
RFID technology is now used in a wide range of sectors, including :
Traceability of medical devices
Patient follow-up in hospital
Stock management by linking your ERP, WMS, LIMS, etc...
Tracking luxury products at events and in boutiques
Animal identification
Badge access control
Laboratory sample location
Asset management
There are many applications, and the types of RFID technology employed vary according to the use case. Detection over distances ranging from a few centimeters to several hundred meters, thanks to a wide range of chips available on the market, whether active or passive... Anything is possible. Here's what you need to know about the particularities of these different systems!
The different RFID systems
Passive RFID
Passive RFID chips chips are the most standardized and inexpensive on the market. As their name suggests, they don't emit waves spontaneously, but are activated only when they receive signals from readers. So they're practical and long-lasting, because they don't need batteries!
Their main features include :
- A range of up to fifteen meters, depending on the size of the chip.
- Low cost, thanks to the absence of a battery and a storage capacity similar to that of a 1D/2D code.
- Their small size makes them adaptable to many situations.
- A consequent lifespan of decades.
Examples of applications Passive RFID is most widely used in warehouses and factories, to facilitate logistics, inventory-taking and inventory management. It can also be found in companies wishing to better manage their assets, as well as in anti-theft systems in stores, or to track books in libraries.
Active RFID
Unlike passive RFID, active chips have theirown power source in the form of a battery. They are characterized by :
- A long range, which can exceed several tens of meters.
- Extended storage capacity.
- A lifespan of around 5 years.
- The need for potential maintenance.
- More expensive than passive RFID.
Application examples Active RFID tags are extremely strategic, as they can detect people and objects over long distances. They are used to track vehicles, people and heavy equipment on construction sites and other industrial sites. They are also practical in difficult conditions, including oil rigs and conflict zones.
Semi-passive RFID
Semi-passive RFID (or semi-active, depending on your point of view) combines the features of the two RFID technologies we've just described. Like the active version, it has a battery. However, it operates in the same way as a passive tag, only triggering when a signal is received from the reader. What's more, as the battery doesn't power the circuit continuously, but only at specific intervals, the system's lifespan is quite high. Here's what you need to know about this technology:
- It has a range of up to 50 metres.
- Its lifespan is between that of active and passive chips.
- More affordable than active versions.
Examples of applications Semi-passive RFID is notably used in supply chains, to trace products, perishables and medicines. It can also be used to check the temperature of goods being transported, to ensure that the cold chain is respected. It's also a great ally for your fleet management, enabling you to locate chipped vehicles.

SolAsset, SolSample, SolCare...
The importance of RFID frequencies
The concept of RFID is intrinsically linked to that of frequencies. Indeed, each system is characterized by specific value ranges, implying notably differences in range.
Here's a table summarizing the essentials of RFID technology frequencies.
| Frequency type | Operating frequency | Reading distance | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| UHF (Ultra High Frequency) | Between 856 MHz and 960 MHz | Can reach up to 15 meters, ideal for large-scale tracking. | Perfect for inventory management, logistics tracking and applications where long-distance reading is required. |
| HF (High Frequency) | Around 13.56 MHz | Generally up to 50 centimetres, offering a good balance between range and precision. | Commonly used for access cards, ticketing and applications requiring closer interaction, such as contactless payments. |
| LF (Low Frequency) | Around 125 kHz to 134 kHz | Limited to a few centimetres, perfect for proximity applications. | Mainly used for access control, pet tracking and medical applications, where a very short range reading is sufficient. |
RFID technology components and operation
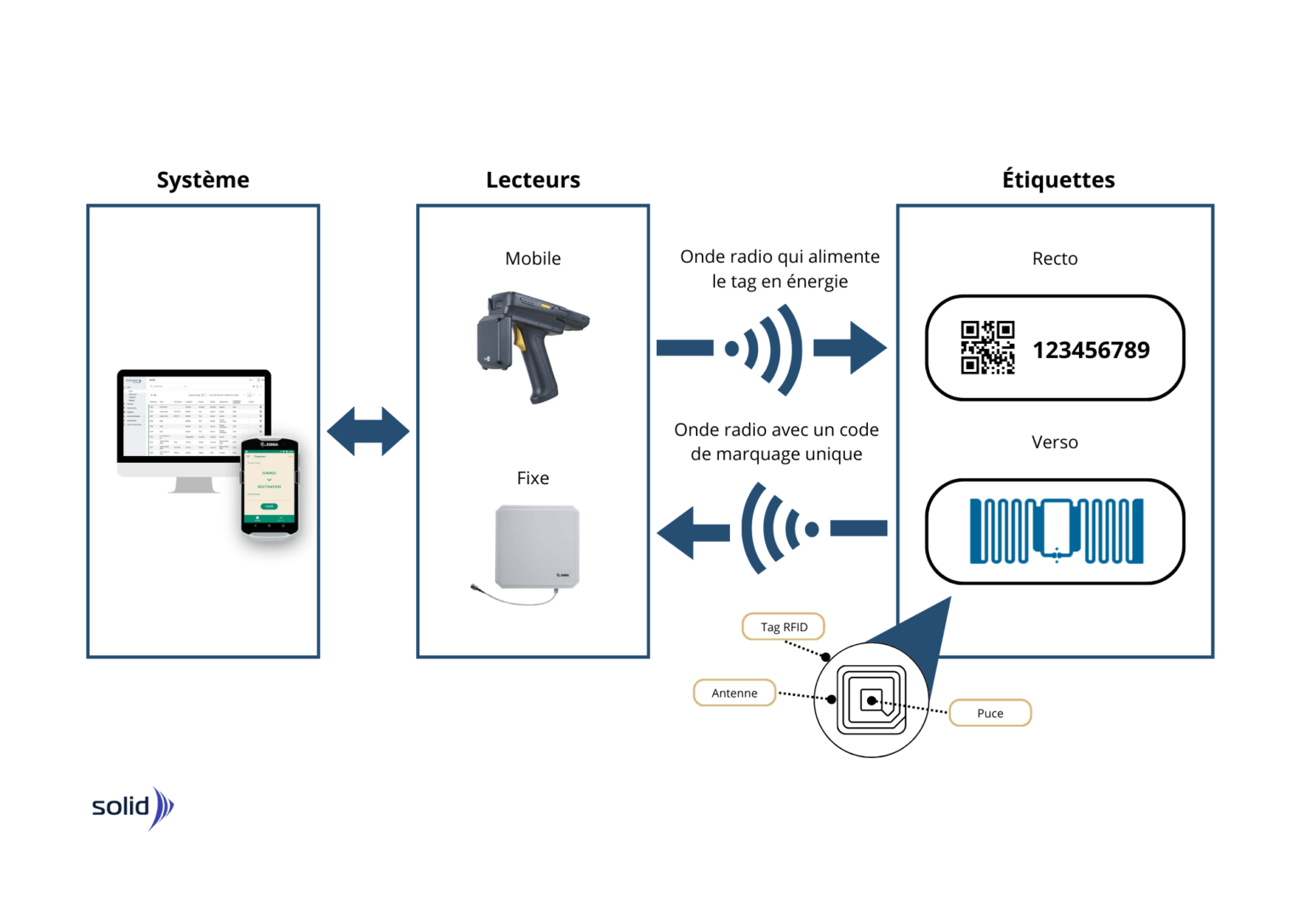
RFID technology is based on communication between the RFID tag and the reader. Let's take a closer look at these components.
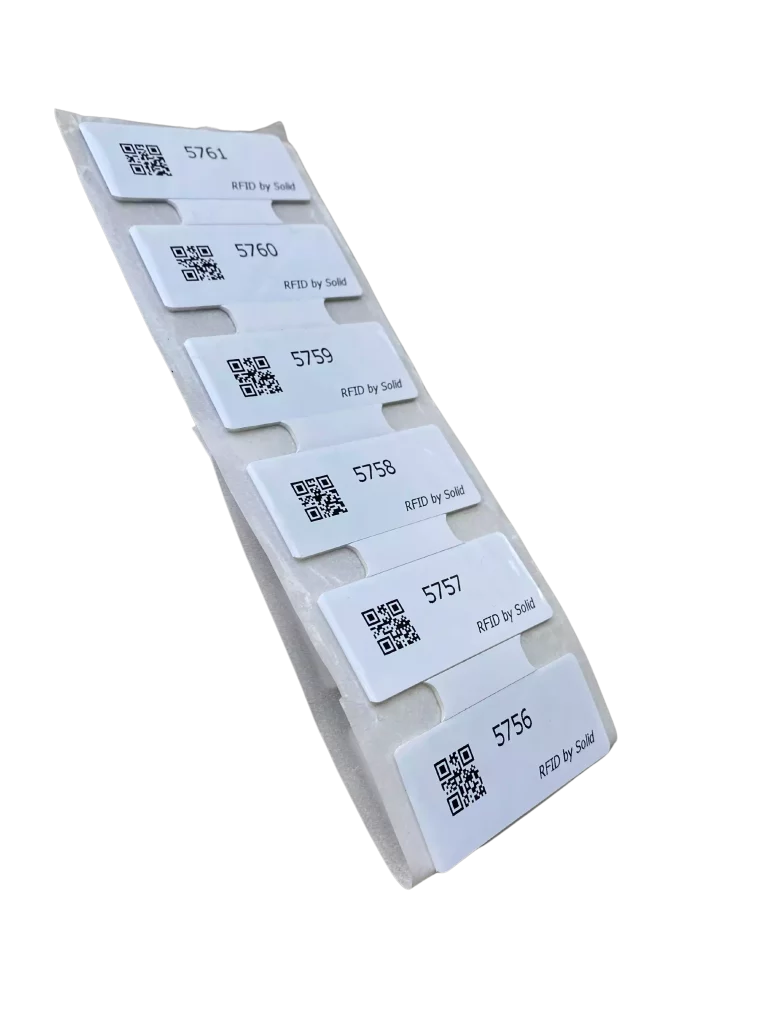
RFID tags
RFID tags take the form ofa microchip, containing an integrated circuit on which a variety of information is stored. They also include an antenna and, for active and semi-active tags, a battery. The combination of chip and antenna is called an inlay. Only when the inlay is associated with an identifier do we speak of a tag.
These RFID tags are configured by means ofa unique identifier, enabling them to be distinguished from others. Of course, depending on the nature of your needs, there are also special chips available. Some can be designed to capture temperatures, others can be made to withstand extreme conditions, and so on...



RFID antennas
As mentioned above, RFID antennas act as an intermediary with readers, enabling remote activation of chips. In fact, the waves they emit are received by the tags, which in turn send radio signals back to them. Although they can't read and process information, they are ideal for extending the range of tags, which have a limited transmission distance. Depending on their size and positioning, they can be used to create high-performance RFID systems.
RFID readers
RFID tags contain information, but only if it can be read. This is precisely the role of readers, whose mission is to convert radio waves into digital data that can be understood and used by your software. Fixed or portable versionsFixed or portable versions, in the form of kiosks, scanners or gantries: it all depends on your objectives and the system you want to set up.
Of course, tags, antennas and readers are not an end in themselves. Whether you work in a production plant, a warehouse, a luxury boutique or a hospital, your goal is to be able to process the data captured by RFID technology. That's where your software comes in.
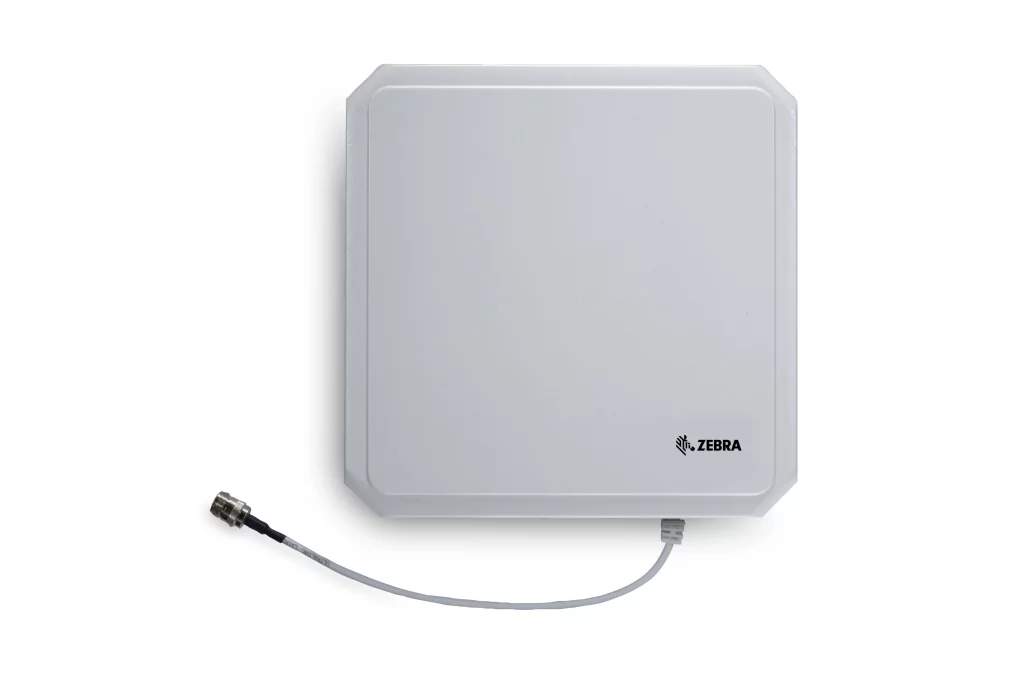
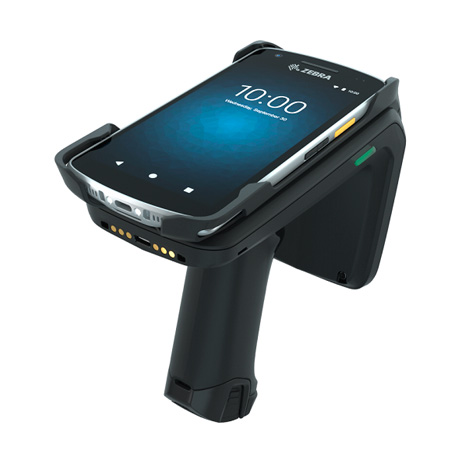



Software
RFID software is essential for interpreting the data captured by readers. It transforms RFID signals into usable information and integrates them into existing data management systems.
In such cases, there are several options open to you. You can opt for a customized software solution. Or, if you don't want yet another software package, a middleware solution can be developed. This middleware will act as a gateway between the data received by the readers and your ERP, WMS, LIMS, etc. It will transform the information received so that you can exploit it directly from your existing solution.
How can you integrate RFID technology into your business?
Opting for an RFID system can indeed revolutionize the way you operate, as part of your drive for operational excellenceand continuous improvement. That said, depending on the size of your organization, implementing such a solution is not always easy. Fortunately, our teams are here to help you from A to Z!
Here are the steps we follow to complete this task.

We assess your needs. First, we take a close look at your company's challenges, to define the extent to which RFID technology can improve your day-to-day business. From asset tracking to optimizing your production lines, from inventory management to tracking people and vehicles, we look at all the possibilities and support you in implementing the best possible strategy.

We'll guide you towards the most efficient RFID technology. As we've seen, the diversity of chips, frequencies and hardware makes choosing the right elements a complex task. As experts in this field, we're here to guide you towards the systems best suited to your needs and budget.

We design a complete RFID system. Once we've identified your needs and chosen the right technology, we design the solution in the field. We define the different flows to be tracked, to create a network that fits in perfectly with existing systems.

We set up and test the network. Once we have agreed with you on the project planning, the selection of elements and their layout, we can move on to the actual implementation. This major deployment will then be followed by pilot tests and technical adjustments, to ensure that the system works perfectly.

We train and sensitize your teams. As you know, the integration of new technologies into the company can only be successful if change management is strong. That's why we offer comprehensive training courses to help your teams familiarize themselves with RFID. We also devote a significant part of this phase to data security, which is essential when it comes to handling information.

We keep your systems up and running. Because your RFID systems need to evolve with your business, we make sure they meet your needs on an ongoing basis, and retain their original efficiency. That's why we offer maintenance services for your technologies, and troubleshooting in the event of any problems.
Your questions about RFID
What's the difference between RFID and NFC chips?
The term NFC chip is probably more familiar to your ears than RFID. But what's the difference? Simple: NFC, or Near Field Communication, is a form of high-frequency RFID. In fact, it enables secure, two-way communication over short distances, generally less than 10 cm.
We use it mainly for mobile or contactless payments, but also for transferring information between two devices equipped with this technology, or for precise geolocation of your stocks or finished products in store.
How are RFID systems secured?
Since RFID involves the transfer of data, data security is essential to prevent data leakage. One thing's for sure: if you're not careful, and a malicious person enters your premises equipped with an RFID reader, they'll be able to intercept your information. To prevent this, the right software can be installed to encrypt tag data.
As is the case with all technologies, obsolete elements often display security flaws that need to be eradicated. And don't forget to make sure your teams are fully aware of the security challenges you face!
Now that you know more about RFID technology and its challenges, don't hesitate to make this choice for your business. Not only will it help you boost performance, it will also increase customer satisfaction. How do you go about it? Nothing could be simpler: contact us to discuss your project!